The Evolution of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
- Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
- A Historical Overview of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
- The Role of Consensus Mechanisms in Securing Blockchain Networks
- Comparing Proof of Work and Proof of Stake Consensus Models
- Exploring Emerging Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
- Challenges and Future Trends in Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain consensus mechanisms are fundamental to the operation of blockchain networks. These mechanisms are responsible for ensuring that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the ledger. Understanding the basics of blockchain consensus mechanisms is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the inner workings of this revolutionary technology.
One of the most common blockchain consensus mechanisms is Proof of Work (PoW). In a PoW system, participants, known as miners, compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process requires a significant amount of computational power, making it secure but energy-intensive.
Another popular consensus mechanism is Proof of Stake (PoS). In a PoS system, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold. This mechanism is more energy-efficient than PoW but still ensures the security of the network.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a variation of the PoS mechanism where token holders vote for delegates to validate transactions on their behalf. This system is known for its scalability and speed, making it ideal for high-traffic blockchain networks.
Understanding the differences between these consensus mechanisms is essential for anyone looking to participate in or build on blockchain networks. Each mechanism has its strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one can have a significant impact on the performance and security of a blockchain network. By delving into the basics of blockchain consensus mechanisms, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the innovative technology that underpins cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications.
A Historical Overview of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
Blockchain consensus algorithms have undergone significant evolution since the inception of blockchain technology. These algorithms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain network by enabling nodes to agree on the validity of transactions.
One of the earliest consensus algorithms used in blockchain technology is Proof of Work (PoW). PoW requires network participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. While PoW is effective in securing the network, it is energy-intensive and can lead to centralization as miners with more computational power have a higher chance of mining new blocks.
To address the limitations of PoW, the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm was introduced. In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold. This reduces energy consumption and promotes decentralization, as validators are incentivized to act in the best interest of the network to protect their investment.
Another notable consensus algorithm is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), which combines the efficiency of PoS with a more democratic governance model. DPoS allows token holders to vote for delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. This system is faster and more scalable than PoW and PoS, making it ideal for applications that require high transaction throughput.
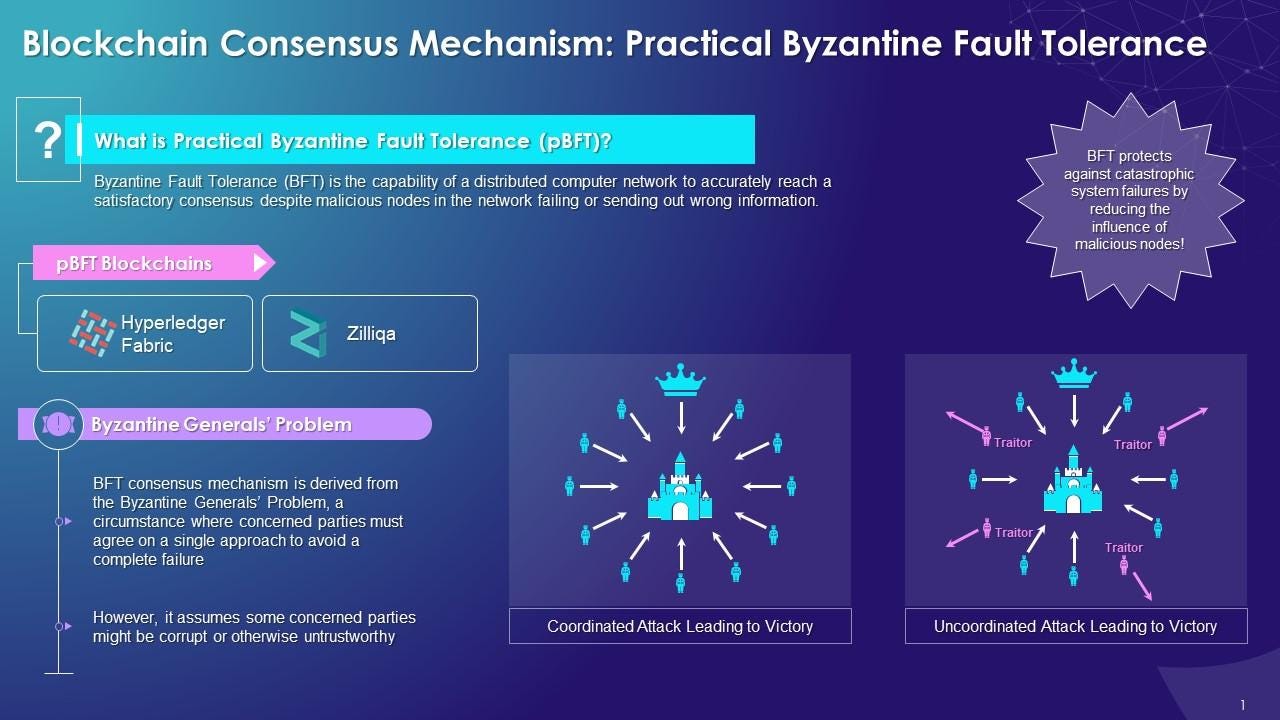
More recently, the emergence of consensus algorithms such as Proof of Authority (PoA) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) has further expanded the possibilities for blockchain networks. PoA relies on a set of approved validators to create new blocks, while PBFT enables consensus to be reached even in the presence of malicious actors.
Overall, the evolution of blockchain consensus algorithms has been driven by the need for scalability, efficiency, and security. As blockchain technology continues to mature, new consensus algorithms are likely to emerge, further enhancing the capabilities of decentralized networks.
The Role of Consensus Mechanisms in Securing Blockchain Networks
Blockchain networks rely on **consensus mechanisms** to ensure the security and integrity of transactions. These mechanisms play a crucial role in validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain. By reaching an agreement on the validity of transactions, **consensus mechanisms** prevent double-spending and other fraudulent activities on the network.
One of the most common **consensus mechanisms** used in blockchain networks is Proof of Work (PoW). In a PoW system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires a significant amount of computational power, making it secure but energy-intensive.
Another popular **consensus mechanism** is Proof of Stake (PoS), where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold. PoS is more energy-efficient than PoW but still ensures the security of the network. Other **consensus mechanisms** such as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA) offer variations on these models to achieve consensus.
Each **consensus mechanism** has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of mechanism can impact the security, scalability, and decentralization of a blockchain network. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, new **consensus mechanisms** are being developed to address these challenges and improve the overall efficiency of blockchain networks. By understanding the role of **consensus mechanisms** in securing blockchain networks, we can better appreciate the importance of these mechanisms in the broader ecosystem.
Comparing Proof of Work and Proof of Stake Consensus Models
When comparing Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus models in blockchain technology, it is essential to understand the fundamental differences between the two. PoW, which is the original consensus algorithm used in Bitcoin, requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process consumes a significant amount of computational power and electricity.
On the other hand, PoS operates on a different principle where validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This eliminates the need for mining and significantly reduces energy consumption. PoS is also considered to be more environmentally friendly compared to PoW.
While PoW is known for its security and proven track record, PoS is gaining popularity due to its energy efficiency and scalability. PoS also incentivizes validators to act in the best interest of the network by penalizing malicious behavior. However, critics argue that PoS may lead to centralization as validators with more coins have more influence over the network.
Exploring Emerging Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
Exploring the various emerging consensus mechanisms in blockchain technology is crucial for understanding the evolution of this revolutionary technology. Consensus mechanisms play a vital role in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain networks by enabling nodes to agree on the validity of transactions. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, new consensus mechanisms are being developed to address the limitations of existing ones and improve the overall efficiency and scalability of blockchain networks.
One of the most well-known consensus mechanisms is Proof of Work (PoW), which is used by popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. However, PoW has been criticized for its high energy consumption and scalability issues. As a result, new consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Proof of Authority (PoA) have emerged as alternatives.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is gaining popularity due to its energy efficiency and reduced centralization risks compared to PoW. In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold, incentivizing them to act in the best interest of the network. On the other hand, Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) introduces a democratic voting system where coin holders elect delegates to validate transactions on their behalf.
Another emerging consensus mechanism is Proof of Authority (PoA), which relies on a set of approved validators to create new blocks. PoA is known for its high throughput and low transaction costs, making it suitable for enterprise blockchain applications. By exploring these emerging consensus mechanisms, blockchain developers can choose the most appropriate mechanism for their specific use case, taking into account factors such as security, scalability, and decentralization.
Challenges and Future Trends in Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the challenges and future trends in blockchain consensus mechanisms are becoming increasingly important to consider. One of the main challenges facing blockchain consensus mechanisms is scalability. As the number of transactions on a blockchain network increases, the time it takes to reach a consensus can slow down significantly. This can lead to delays in transaction processing and higher fees for users.
Another challenge is the issue of energy consumption. Many blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin, rely on proof-of-work mechanisms that require a significant amount of computational power to validate transactions. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology and has led to the development of more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.
Looking towards the future, there are several trends emerging in blockchain consensus mechanisms. One of these trends is the move towards proof-of-stake mechanisms, which rely on validators holding a stake in the network to reach consensus. This can help reduce energy consumption and improve scalability compared to proof-of-work mechanisms.
Another trend is the development of hybrid consensus mechanisms that combine different approaches to achieve a balance between security, scalability, and decentralization. These hybrid mechanisms aim to take advantage of the strengths of different consensus algorithms while mitigating their weaknesses.
In conclusion, the challenges and future trends in blockchain consensus mechanisms are shaping the way blockchain technology will be used in the years to come. By addressing scalability issues, reducing energy consumption, and exploring new consensus mechanisms, blockchain networks can become more efficient, secure, and sustainable.
