The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
- Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
- Challenges and Opportunities of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chains
- Exploring the Potential Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management
- Case Studies: How Companies are Leveraging Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
- The Impact of Blockchain on Traceability and Counterfeit Prevention in Supply Chains
- Predictions for the Future of Blockchain Integration in Supply Chain Management
Understanding the Role of Blockchain in Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing transparency, security, and efficiency throughout the entire process. By utilizing a decentralized ledger system, blockchain can track every step of the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to the final product delivery.
One of the key benefits of blockchain in supply chain management is its ability to create an immutable record of transactions. This means that once data is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity of the information. This level of transparency helps to build trust among all parties involved in the supply chain.
Another advantage of blockchain is its ability to streamline processes and reduce costs. By automating tasks such as verification, payment processing, and compliance checks, blockchain can eliminate the need for intermediaries and paperwork, saving time and resources.
Furthermore, blockchain technology can enhance traceability in the supply chain, allowing companies to track the origins of products and verify their authenticity. This is particularly important in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where safety and quality are paramount.
In conclusion, blockchain has the potential to transform supply chain management by improving transparency, security, and efficiency. As more companies adopt this technology, we can expect to see significant improvements in the way goods are sourced, produced, and delivered to consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities of Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chains
Implementing blockchain in supply chains presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses looking to enhance their operations. One of the main challenges is the complexity of integrating blockchain technology into existing systems. This process requires significant time and resources to ensure seamless integration without disrupting current operations. However, the opportunities that blockchain offers in terms of increased transparency, security, and efficiency far outweigh these challenges.
One of the key opportunities of implementing blockchain in supply chains is the ability to create a transparent and immutable record of transactions. This can help businesses track the movement of goods from the source to the end consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing the risk of fraud. Additionally, blockchain can streamline processes such as inventory management, payment processing, and contract execution, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Another opportunity that blockchain presents is the potential for increased collaboration and trust among supply chain partners. By sharing a decentralized ledger, businesses can establish a single source of truth that all parties can access and verify. This can help reduce disputes, improve communication, and build stronger relationships within the supply chain ecosystem.
Despite these opportunities, businesses must also be aware of the challenges that come with implementing blockchain in supply chains. One such challenge is the need for standardization and interoperability among different blockchain platforms. Without a common set of protocols and standards, businesses may struggle to communicate and transact with partners using different blockchain systems.
Furthermore, businesses must also consider the scalability and security implications of implementing blockchain in their supply chains. As the volume of transactions increases, so does the strain on the blockchain network. Businesses must ensure that their chosen blockchain platform can handle the volume of transactions required for their operations while maintaining the security and integrity of the data stored on the blockchain.
In conclusion, while there are challenges to overcome, the opportunities presented by implementing blockchain in supply chains are vast. By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses can improve transparency, efficiency, and trust within their supply chain operations, ultimately leading to a more resilient and competitive business ecosystem.
Exploring the Potential Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing transparency, security, and efficiency throughout the entire process. By utilizing blockchain, companies can track products from their origin to the final destination, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeit goods from entering the market.
One of the key benefits of blockchain in supply chain management is the ability to create a decentralized ledger that is immutable and transparent. This means that all parties involved in the supply chain can access real-time information about the movement of goods, leading to increased trust and collaboration among stakeholders.
Moreover, blockchain technology can streamline processes such as inventory management, payments, and contract enforcement by automating tasks through smart contracts. This not only reduces the risk of errors and fraud but also speeds up the overall supply chain operations.
Another advantage of implementing blockchain in supply chain management is the enhanced security it provides. By encrypting data and storing it across multiple nodes, blockchain makes it nearly impossible for hackers to tamper with information, ensuring the integrity of the supply chain.
In conclusion, the potential benefits of blockchain technology in supply chain management are vast and can lead to a more efficient, transparent, and secure system. As companies continue to explore the possibilities of blockchain, we can expect to see significant improvements in how goods are tracked, verified, and delivered to consumers.
Case Studies: How Companies are Leveraging Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Several companies have successfully implemented blockchain technology to enhance transparency in their supply chains. By leveraging blockchain, these companies have been able to track products from their origin to the final destination, ensuring authenticity and reducing the risk of fraud. Let’s take a look at some case studies of how companies are utilizing blockchain for improved supply chain management:
- Walmart: The retail giant has partnered with IBM to implement blockchain technology in its food supply chain. By using blockchain, Walmart can trace the journey of a product from the farm to the store shelves, providing customers with detailed information about the product’s origins and quality.
- Maersk: The shipping company Maersk has also adopted blockchain to streamline its supply chain operations. By digitizing its documentation process using blockchain, Maersk has been able to reduce paperwork, minimize errors, and improve overall efficiency in tracking shipments.
- De Beers: The diamond company De Beers is using blockchain to provide transparency in its diamond supply chain. By recording each diamond’s journey on a blockchain ledger, De Beers can ensure that its diamonds are ethically sourced and conflict-free, giving customers peace of mind.
These case studies demonstrate the diverse ways in which companies are leveraging blockchain technology to enhance transparency and efficiency in their supply chains. As more companies recognize the benefits of blockchain in supply chain management, we can expect to see widespread adoption of this technology across various industries in the future.
The Impact of Blockchain on Traceability and Counterfeit Prevention in Supply Chains
Blockchain technology has revolutionized traceability and counterfeit prevention in supply chains. By leveraging the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain, companies can now track products from their origin to the end consumer with unprecedented transparency and security. This has significantly reduced the risk of counterfeit products entering the supply chain, protecting both consumers and brands from potential harm.
One of the key advantages of blockchain in traceability is its ability to create a tamper-proof record of every transaction that occurs within the supply chain. Each step in the production and distribution process is recorded on a block, which is then linked to the previous block, creating a chain of information that is secure and unchangeable. This ensures that all parties involved in the supply chain have access to real-time data on the movement of goods, enabling quick identification of any discrepancies or irregularities.
Moreover, blockchain technology enables the implementation of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This allows for automated verification of transactions and compliance with predefined rules, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human error or fraud. Smart contracts can also trigger alerts or notifications in case of any unauthorized activity, enabling swift action to be taken to prevent counterfeit products from entering the supply chain.
In addition to traceability and counterfeit prevention, blockchain also enhances supply chain management by improving efficiency and reducing costs. By streamlining processes and eliminating intermediaries, blockchain technology can help companies optimize their operations and achieve greater visibility and control over their supply chains. This can lead to faster delivery times, lower inventory costs, and improved overall performance, ultimately benefiting both businesses and consumers alike.
Overall, the impact of blockchain on traceability and counterfeit prevention in supply chains is undeniable. As companies continue to adopt this transformative technology, the future of supply chain management looks brighter than ever, with increased transparency, security, and efficiency paving the way for a more sustainable and trustworthy global marketplace.
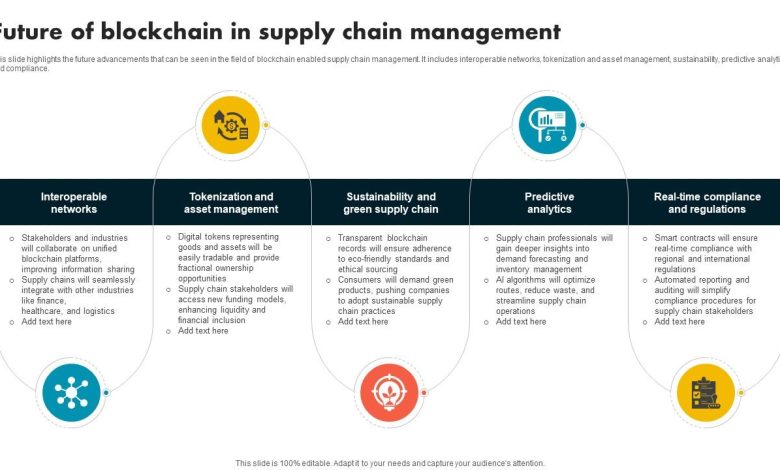
Predictions for the Future of Blockchain Integration in Supply Chain Management
The future of blockchain integration in supply chain management looks promising as more companies are recognizing the benefits of utilizing this technology. Here are some predictions for how blockchain will continue to revolutionize supply chain management:
- Increased transparency: Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain. This increased visibility can help reduce fraud and errors.
- Enhanced traceability: With blockchain, each transaction is recorded and time-stamped, allowing for easy traceability of products. This can be especially useful in industries where tracking the origin of goods is crucial.
- Improved security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it less vulnerable to cyber attacks and data breaches. This added layer of security can help protect sensitive information within the supply chain.
- Streamlined payments: Blockchain technology can facilitate faster and more secure payments between parties in the supply chain. Smart contracts can automatically execute payments when certain conditions are met, reducing delays and disputes.
- Efficient inventory management: By using blockchain to track inventory levels in real-time, companies can optimize their supply chain operations and reduce excess inventory. This can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Overall, the integration of blockchain in supply chain management is expected to continue growing as companies seek to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance trust among partners. By leveraging the benefits of blockchain technology, businesses can stay competitive in an increasingly complex global marketplace.
